Choosing the right casting process can make or break your project. Two popular methods, sand casting and die casting, offer unique advantages and challenges. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? Let’s dive into a detailed comparison to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding Sand Casting
What Is Sand Casting?
Sand casting is one of the oldest manufacturing techniques, dating back thousands of years. This process involves pouring molten metal into a mold made of sand to create a desired shape. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? It’s widely used for producing large and complex parts.
How Sand Casting Works
The process begins with a sand mold created using a pattern. The mold cavity is formed, and molten metal is poured into it. Once the metal solidifies, the mold is broken to retrieve the casting. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? The steps include:
- Preparing the sand mold
- Melting and pouring metal
- Allowing it to cool and solidify
- Breaking the mold and finishing the product
Advantages of Sand Casting
- Versatility: Handles a wide range of metals, including ferrous and non-ferrous alloys Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project?
- Cost-effective for Low Volumes: Perfect for prototyping and small batches.
- Customizable: accommodates intricate and oversized designs.
Limitations of Sand Casting
- Surface Finish: Rough texture often requires post-processing.
- Tolerances: Less precision compared to other methods.
- Longer Production Time: Slower due to mold preparation and cooling.
Understanding Die Casting

What Is Die Casting?
Die casting is a highly efficient process for creating precise metal parts. It involves forcing molten metal into reusable steel molds under high pressure. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? This method is commonly used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
How Die Casting Works
The process uses a metal die to form parts with high accuracy. Key steps include:
- Preparing the steel die
- Heating the metal to a molten state
- Injecting the molten metal into the die under pressure
- Cooling and ejecting the final product
Advantages of Die Casting
- High Precision: Produces parts with tight tolerances.
- Smooth Surface Finish: Often eliminates the need for machining.
- Mass Production Efficiency: Ideal for large-scale production.
Limitations of Die Casting
- High Initial Cost: Tooling and die setup can be expensive.
- Material Limitations: Limited to non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project?
- Complexity Constraints: Not suitable for extremely intricate designs.

When it comes to metal casting, choosing the right method is crucial to achieving the desired quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Two of the most common casting methods are sand casting and die casting. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different types of projects. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? Let’s break down the differences and help you decide which one suits your project best.
Sand Casting: Overview and Advantages
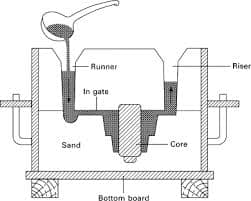
Sand casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold made of sand. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? It’s one of the oldest and most versatile casting methods. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? Here are its key features:
Advantages:
- Versatility: Suitable for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
- Cost-Effective for Small Batches: Ideal for low-volume production.
- Complex Geometries: Can produce intricate shapes and large-sized castings.
- Lower Tooling Costs: Molds are inexpensive and easy to modify.
Disadvantages:
- Surface Finish: Rougher compared to die casting.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Lower precision, requiring machining after casting.
- Longer Production Time: Molds need to be rebuilt for each cast.
- Mechanical Properties: Slightly lower compared to die-cast parts.
Applications of Sand Casting:
- Engine blocks and cylinder heads
- Pump housings
- Machine bases
- Sculptures and artistic pieces
- Heavy industrial components
Die Casting: Overview and Advantages
Die casting involves forcing molten metal into a metal mold (die) under high pressure. It’s known for producing high-precision parts at high volumes.
Advantages:
- High Precision and Accuracy: Produces detailed and consistent parts.
- Smooth Surface Finish: Requires little to no post-processing.
- Rapid Production Rate: Ideal for mass production.
- Strength and Durability: High-density and robust parts.
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Costs: Dies are expensive to manufacture.
- Material Limitations: Primarily used for non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium.
- Size Limitations: Less suitable for very large components.
- Complexity: Not as adaptable to complex geometries as sand casting.
Applications of Die Casting:
- Automotive components (e.g., engine blocks, transmission cases)
- Electronic housings
- Appliance parts
- Hardware and fittings
- Precision instruments
Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Key Differences
| Aspect | Sand Casting | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Low to Medium | High |
| Cost Efficiency | Low for large volumes, high for small | High for mass production |
| Surface Finish | Rough | Smooth, precise |
| Tooling Costs | Low | High |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Material Flexibility | Ferrous and Non-ferrous | Mostly Non-ferrous (aluminum, zinc) |
Which One Suits Your Project?
Choosing between sand casting and die casting depends on your project requirements:
- Go for Sand Casting if:
- You need large or complex shapes.
- Production volume is low to medium.
- Cost is a primary concern.
- The material required is ferrous (like cast iron or steel).
- Choose Die Casting if:
- High production volume justifies tooling costs.
- Precision and smooth surface finish are critical.
- You are working with non-ferrous metals.
- Strength and uniformity are essential.
FAQs
1. What are the main differences between sand casting and die casting?
The key differences include material suitability, surface finish, production volume, and cost. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? Sand casting is more versatile, while die casting is precise and efficient for large-scale runs.
2. Can both methods be used for the same project?
Yes, but the choice depends on the design, budget, and production needs. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? For prototypes, sand casting is preferred, while die casting suits mass production.
3. Which method is more cost-effective for large-scale production?
Die casting is more economical for large production runs due to its lower per-part cost despite high initial tooling expenses.
4. What factors influence the choice between the two processes?
Key factors include material type, design complexity, production volume, surface finish requirements, and budget.
5. How does the casting method affect product quality?
Die casting delivers higher precision and smoother finishes, while sand casting may require additional finishing for similar quality.
Sources:
Kinematics, G. (2024, June 19). Die Casting vs Sand Casting: What’s the Difference? General Kinematics.
Team, G. (2022, March 21). Die Casting vs. Sand Casting: What is the Difference? Gabrian.
Admin. (2022, November 24). Sand Casting vs. Die Casting vs. Investment Casting. Howard Precision
Conclusion
Both sand casting and die casting offer unique benefits and drawbacks. Sand Casting vs. Die Casting: Which One Suits Your Project? Your choice should be based on factors such as production volume, required accuracy, surface finish, material, and budget. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method will help ensure your project’s success.