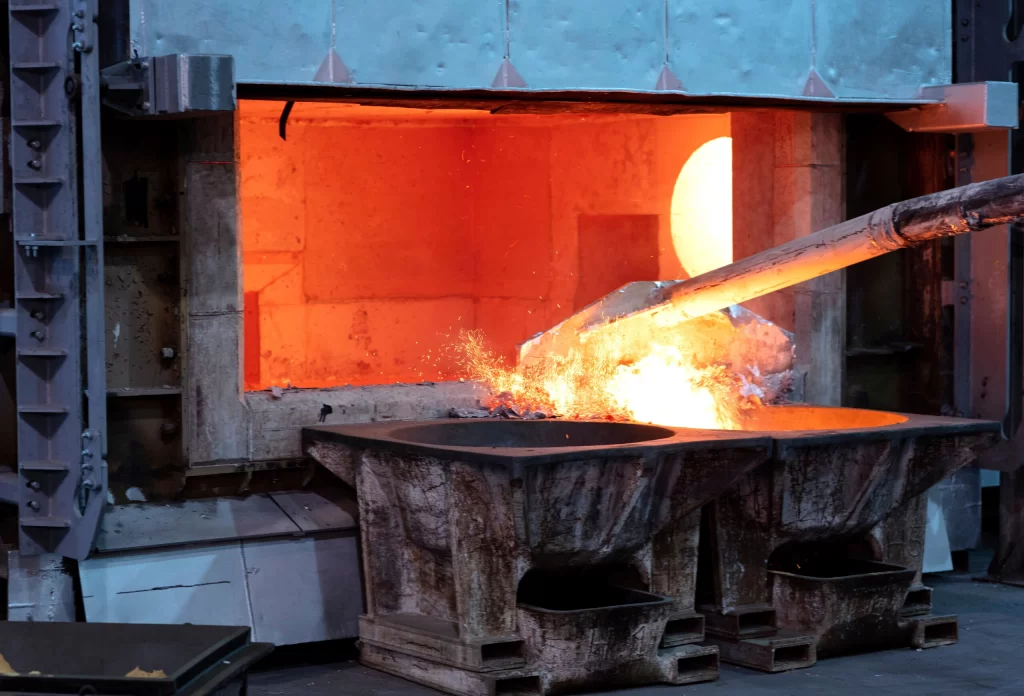
Aluminium Casting
Best Aluminium Casting:
Aluminium Casting is a versatile process used to shape molten aluminium into precise and functional components. Moreover, at CSG Extrusion LLC, we specialize in high-quality aluminium casting for various industries including automotive, aerospace, construction, and more.

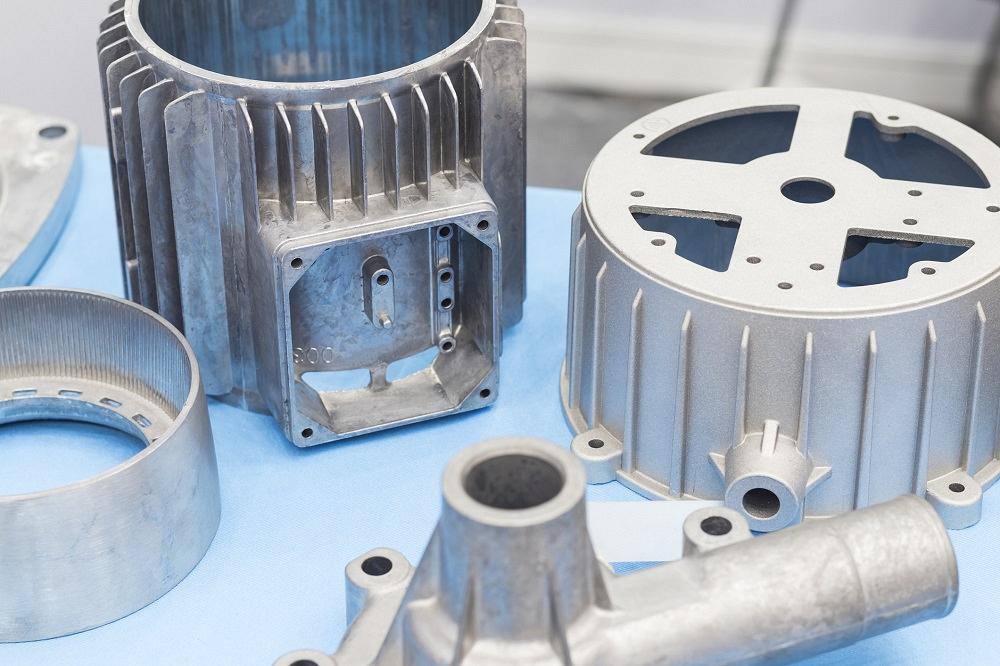
Common Aluminum Casting Methods
1. Die Casting
2. Sand Casting
3. Investment Casting (Lost Wax)
4. Permanent Mold Casting
5. Centrifugal Casting
6. Gravity Die Casting
7. Vacuum Casting
Factors to Consider in Aluminum Casting
1. Part Complexity
Firstly, Investment or die casting handles complex, detailed shapes exceptionally well.
On the other hand, sand or gravity casting is more suitable for basic, straightforward designs.
2. Production Volume
When it comes to scale, for large production runs, die casting proves to be the most efficient method in aluminium casting.
Meanwhile, sand or investment casting offers flexibility for smaller batches.
3. Accuracy & Surface Finish
Best finish: Die and investment casting
General use: Sand casting
4. Size of Components
Large parts: Sand or permanent mold casting
Small precision parts: Die or investment casting
5. Mechanical Properties
High strength: Vacuum or centrifugal casting
Standard performance: Most casting methods
6. Budget
On a tight budget? Go for sand casting.
However, if you’re aiming for premium performance at scale, die casting is the way to go.


Applications of Aluminum Casting
Automotive: Engine blocks, gear housings (Die Casting).
Aerospace: Turbine blades, structural parts (Investment, Vacuum Casting).
Construction: Brackets, beams (Sand Casting).
Electronics: Housings, heat sinks (Die Casting).
Machinery: Suitable for high-load parts made with Centrifugal or Permanent Mold Casting.
Advanced Casting Techniques
Low-Pressure Die Casting
Controlled metal flow, minimal defects
Ideal for wheels and structural parts
Squeeze Casting
Combines casting & forging
Superior mechanical properties
Semi-Solid Casting
Reduced porosity, excellent finish
Aerospace & automotive use
Tilt Pour Casting
Minimizes turbulence and inclusions
Perfect for thin-walled component production
